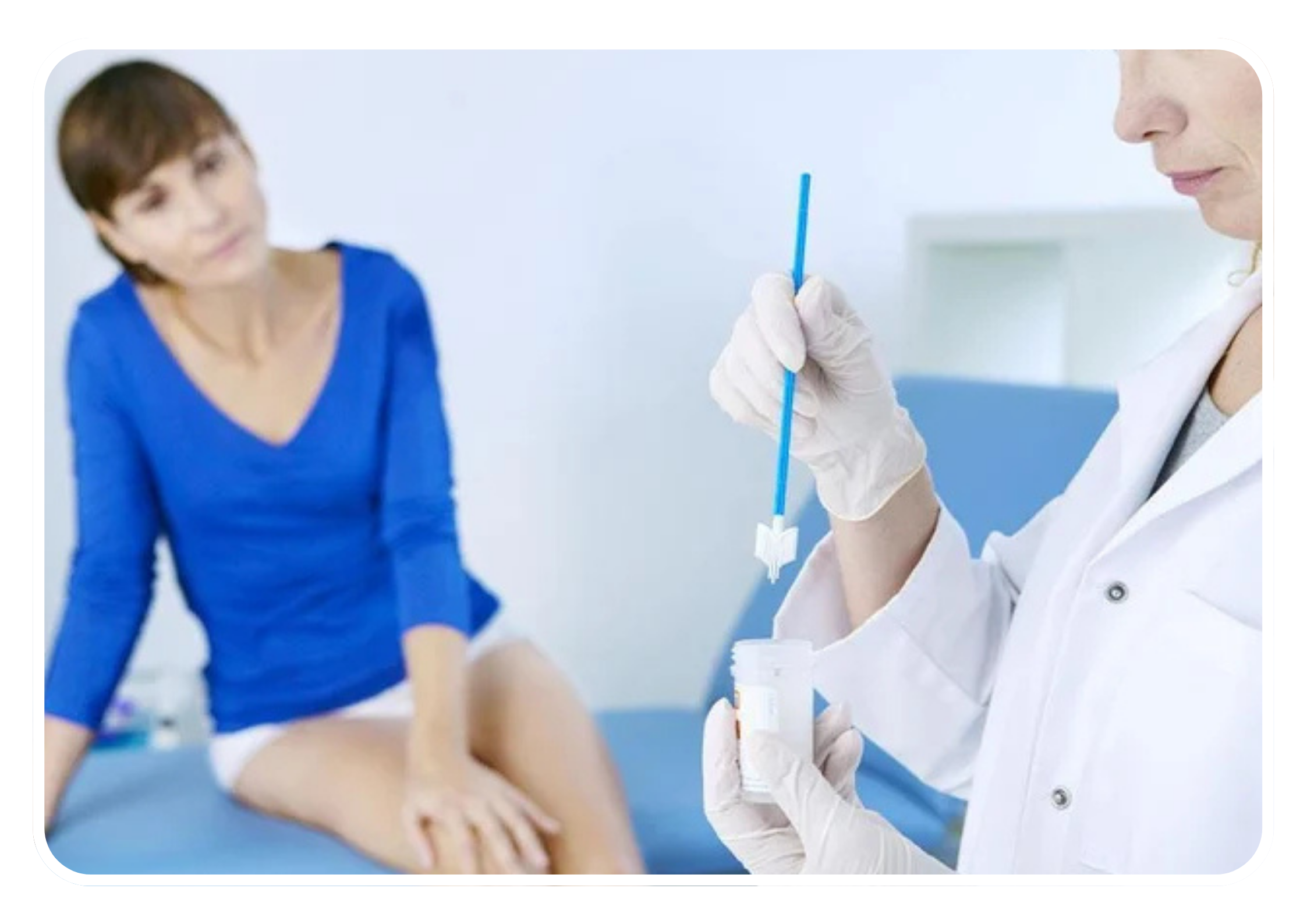
Pap Smear (Pap Test)
- Purpose: Detects abnormal cells on the cervix that may indicate cervical cancer or precancerous changes.
- Procedure: A healthcare provider collects cells from the cervix and sends them to a laboratory for examination.
- Recommendation: Typically recommended starting at age 21 and repeated every three to five years for most women, depending on age and risk factors.
HPV Test
- Purpose: Screens for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) strains associated with cervical cancer.
- Procedure: Often performed in conjunction with a Pap smear.
- Recommendation: Recommended for women aged 30 and older, either alone or in combination with a Pap smear, and may be repeated every five years if results are negative.
Breast Cancer Screening (Mammogram)
- Purpose: Detects breast cancer in its early stages, often before symptoms develop.
- Procedure: X-ray images of the breast tissue are taken and examined for abnormalities.
- Recommendation: Typically recommended for women aged 40 and older, performed annually or biennially depending on individual risk factors.
Breast Self-Examination (BSE)
- Purpose: Helps women become familiar with their breasts to identify any changes.
- Procedure: Regular self-checks for changes such as lumps, thickening, or nipple discharge.
- Note: BSE is no longer recommended as a standalone screening method but can be part of overall breast health awareness.
Clinical Breast Examination (CBE)
- Purpose: Checks for abnormalities in the breasts.
- Procedure: A physical examination of the breasts performed by a healthcare provider.
- Recommendation: May be performed in conjunction with mammography as part of breast cancer screening.
Pelvic Examination
- Purpose: Evaluates the health of the reproductive organs.
- Procedure: A thorough examination of the external and internal reproductive organs, including the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
- Use: Performed as part of routine gynecological care or to evaluate symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or vaginal discharge.
STI Testing
- Purpose: Screens for sexually transmitted infections.
- Procedure: Laboratory tests on samples of blood, urine, or genital swabs.
- Recommendation: Advised for sexually active individuals, particularly those with multiple sexual partners or other risk factors.
Importance of Regular Screening
Regular gynecological screenings are crucial for detecting gynecological conditions early, when they are most treatable. Women should discuss their individual risk factors and screening needs with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate tests and intervals. Regular screenings can lead to early intervention, better management of health issues, and improved overall health outcomes.